Upper Gi Endoscopy
Upper Gi Endoscopy
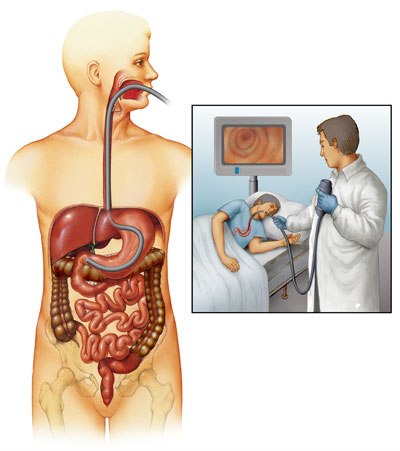
Upper GI Endoscopy is a medical procedure to diagnose problems of your Upper GI Tract. It includes a food pipe, stomach, and part of your small intestine. In endoscopy, a tube-like device with a camera and light at one end is put inside the mouth and throat, following towards the esophagus and stomach, so that the examiner can get a clear view of the GI tract. At the other end of the examiner, there are controls used to pump air into the stomach, clear the view with water or pull out unwanted content. Endoscopy is suggested when the symptoms are unexplained or unresponsive to the medication. It is most commonly done when there is persistent heartburn, upper abdominal pain, intense bleeding from the upper gut, and anemia. Dr. Harshad Joshiis one of the experienced and Best Gastroenterologist in Mumbai.
Upper Gi Endoscopy
Gastroscopy, also known as upper endoscopy or esophagogastroduodenoscopy (EGD), is a medical procedure that involves using a thin, flexible tube with a camera and light source at its tip to examine the inner lining of the upper gastrointestinal tract. The upper gastrointestinal tract includes the esophagus, stomach, and the first part of the small intestine called the duodenum.
During a gastroscopy procedure, a gastroenterologist or a specially trained healthcare professional inserts the endoscope through the mouth and advances it down the throat, guiding it into the esophagus, stomach, and duodenum. The camera at the end of the scope transmits real-time images of the gastrointestinal lining to a monitor, allowing the healthcare provider to visualize the mucosal surface and identify any abnormalities, such as ulcers, inflammation, tumors, or other structural issues.

Gastroscopy serves various purposes, including:
- 1.Diagnosing conditions: It can help diagnose conditions such as gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD), ulcers, gastritis, Barrett’s esophagus, celiac disease, and certain cancers.
2.Treatment: Gastroscopy can be used to perform certain therapeutic procedures, such as removing polyps, taking biopsies, and stopping active bleeding from ulcers.
3.Monitoring: Individuals with certain chronic conditions may require regular gastroscopy to monitor the progression of their disease and assess the effectiveness of treatment.
4.Evaluation: Gastroscopy is often used to investigate symptoms such as persistent heartburn, difficulty swallowing, unexplained weight loss, or gastrointestinal bleeding.
The procedure is usually performed with the patient sedated or under light anesthesia to minimize discomfort. It’s a common and relatively safe procedure, but as with any medical procedure, there are potential risks and complications, such as bleeding, infection, or perforation of the gastrointestinal tract. Patients should follow their healthcare provider’s instructions before and after the procedure to ensure its success and reduce the risk of complications.
