A PEG is a feeding tube inserted into the stomach using a Gastroscope (see diagram). To place the tube, an endoscope (a thin flexible tube with a camera at the end) is passed through your mouth, down the gullet into the stomach.
Percutaneous Endoscopic Gastrostomy
Percutaneous Endoscopic Gastrostomy
A percutaneous endoscopic gastrostomy (PEG) tube placement is a medical procedure that involves the insertion of a feeding tube directly into the stomach through the abdominal wall. PEG tube placement is typically performed using an endoscope, a flexible tube with a camera and light on its tip, which allows healthcare providers to guide the tube into the stomach while visualizing the process on a monitor.
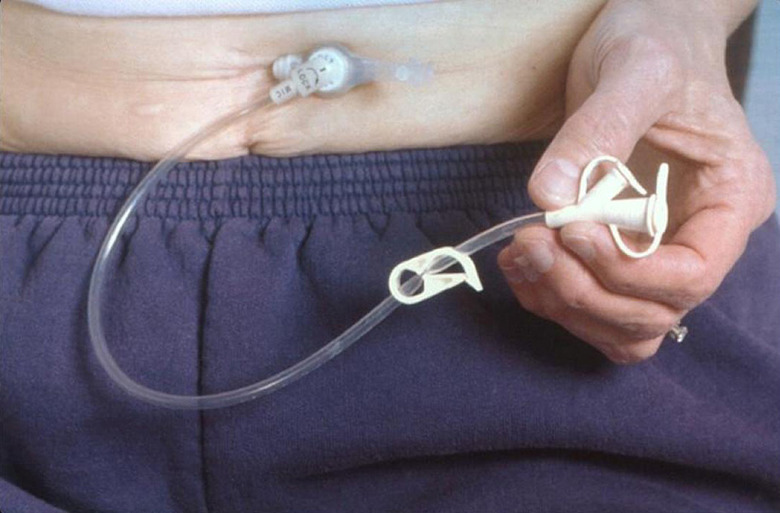
PEG tube placement is commonly used for individuals who are unable to eat or drink adequately due to various conditions, such as neurological disorders, head and neck cancers, or other medical issues that hinder the ability to swallow or take in nutrition orally. PEG tubes provide a means of delivering nutrition, fluids, and medications directly into the stomach
After the procedure, patients are given instructions on how to care for the PEG tube, avoid infections, and administer feeds. Regular follow-up with healthcare providers is necessary to ensure the tube remains in good condition and to monitor the patient’s nutritional status. The PEG tube can be used for short-term or long-term feeding, depending on the patient’s medical needs.
Percutaneous Endoscopic Gastrostomy
Percutaneous endoscopic gastrostomy (PEG) is an endoscopic medical procedure in which a tube (PEG tube) is passed into a patient’s stomach through the abdominal wall, most commonly to provide a means of feeding when oral intake is not adequate (for example, because of dysphagia or sedation). This provides enteral nutrition (making use of the natural digestion process of the gastrointestinal tract) despite

bypassing the mouth; enteral nutrition is generally preferable to parenteral nutrition (which is only used when the GI tract must be avoided). The PEG procedure is an alternative to open surgical gastrostomy insertion, and does not require a general anesthetic; mild sedation is typically used. PEG tubes may also be extended into the small intestine by passing a jejunal extension tube (PEG-J tube) through the PEG tube and into the jejunum via the pylorus.
